ERP introduction highlights the integration of key business processes to enhance efficiency, data access, and collaboration. This post offers CSVTU notes on ERP’s conceptual model, benefits, related technologies, and a comparison with MIS and DSS for a comprehensive understanding.

Q1: What is an enterprise? What are the drawbacks of traditional information systems?
Definition of an Enterprise
An enterprise is a group of people working towards a shared goal by utilizing various resources such as finances, raw materials, technology, and infrastructure. It may be a small business (e.g., a coffee shop) or a large multinational organization like Hindustan Lever. Enterprises are structured to operate as integrated entities where departments collaborate to achieve business objectives.
Drawbacks of Traditional Information Systems
Traditional information systems are often department-specific and isolated, resulting in several operational inefficiencies. Below are the key drawbacks:
| Drawback | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Silos | Departments store and manage their own data separately, leading to duplication and inconsistency. |
| Poor Communication | Limited or no sharing of data across departments causes delays in collaboration. |
| Delayed Decisions | Critical information reaches only top management, making real-time operational decisions difficult. |
| Conflicting Objectives | Departments may have opposing goals; e.g., sales wants product variety, while production prefers standardization to reduce costs. |
| Increased Errors | Manual data exchange between departments increases error rates and operational risks. |
Example: In a traditional system, the production department may not have access to real-time sales data, causing delays in inventory replenishment.
Traditional systems hinder organizational efficiency and competitiveness, which is why modern enterprises increasingly rely on integrated systems like ERP.
Q2: Draw and explain the general or conceptual model of ERP. (What is ERP? Explain the conceptual model of ERP with its benefits.)
Definition of ERP
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is an integrated business management system that consolidates core functions—finance, sales, supply chain, human resources—into a unified data platform. ERP enables cross-functional collaboration and real-time access to data, ensuring efficient operations.
Conceptual Model of ERP
The conceptual model of ERP is built on five key components:
| ERP Model Components | Description |
|---|---|
| Flat Organization | Reduces complex hierarchies, allowing faster communication and decision-making. |
| Make-to-Order Philosophy | Focuses on producing goods/services based on real demand instead of large inventories. |
| Empowered Employees | Provides employees with access to necessary data and tools to improve their productivity. |
| Customer-Supplier Integration | Connects external stakeholders like suppliers and customers to core business processes. |
| Advanced IT Infrastructure | Leverages technologies like cloud computing, automation, and analytics for real-time data access. |
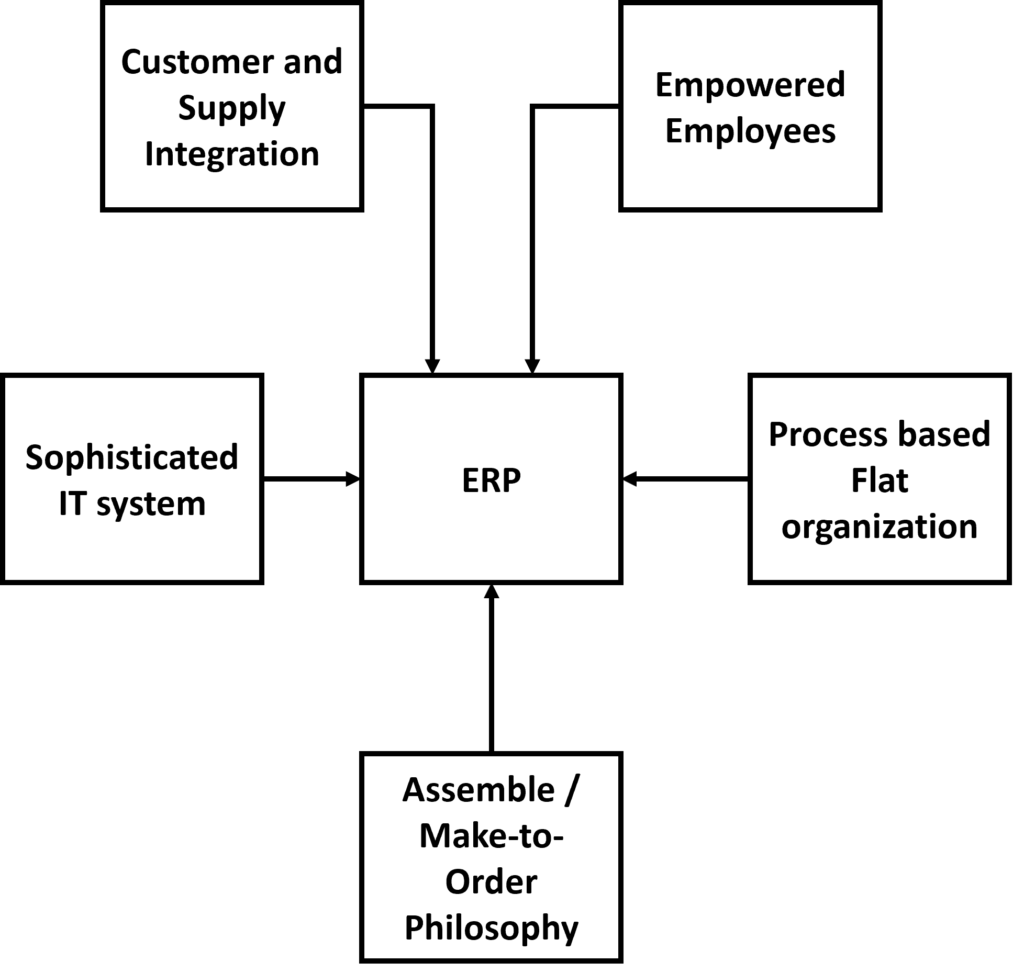
ERP Model Flow Example
Consider an order management process:
- Customer places an order → The system checks inventory levels in real-time.
- Production scheduling → If stock is insufficient, production is initiated.
- Procurement → Raw materials are ordered automatically based on production needs.
- Order tracking → The customer can track the order’s progress at each stage.
This integration ensures seamless communication between departments and stakeholders.
Benefits of ERP
- Centralized Data Management:
All departments access and update a single source of real-time data, reducing errors. - Operational Efficiency:
Automated workflows streamline processes like order fulfillment, inventory management, and financial reporting. - Improved Collaboration:
Departments share data, enhancing coordination and reducing conflicts. - Informed Decision-Making:
Real-time analytics provide insights into business performance, enabling quick, data-driven decisions. - Scalability:
ERP systems can grow with the business, accommodating new operations, departments, and market expansions.
Q3: Write the advantages and disadvantages of ERP.
Advantages of ERP
| Advantage | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Improved Resource Management | Optimizes the use of resources like inventory, workforce, and finances. |
| Customer Satisfaction | Faster response times and real-time order tracking enhance the customer experience. |
| Automation of Processes | Reduces manual intervention and errors through automated workflows. |
| Transparency | Real-time visibility into operations promotes accountability and performance monitoring. |
| Scalable Architecture | ERP systems can support organizational growth and new business models. |
Disadvantages of ERP
| Disadvantage | Explanation |
|---|---|
| High Costs | Implementing ERP involves significant expenses for software, hardware, and training. |
| Complex Implementation | Requires extensive planning, organizational change, and resource allocation. |
| Customization Challenges | Off-the-shelf ERP systems may not fit all business needs, leading to costly customizations. |
| Employee Resistance | Employees may be reluctant to adopt new workflows without proper training and change management. |
| Vendor Dependence | Organizations may need ongoing support from vendors or consultants for updates and maintenance. |
Q4: What are the technologies employed to overcome the limitations of ERP?
To overcome ERP’s limitations, several complementary technologies have been developed. These technologies enhance ERP functionality and improve data analysis, collaboration, and process automation.
Technologies Enhancing ERP
| Technology | Function |
|---|---|
| Business Process Reengineering (BPR) | Redesigns and optimizes business processes for ERP integration. |
| Management Information System (MIS) | Provides structured reports and insights to support routine decision-making. |
| Data Warehousing (DWH) | Stores large volumes of historical data for business intelligence and trend analysis. |
| Data Mining and OLAP | Identifies patterns and trends by analyzing multi-dimensional data sets. |
| Supply Chain Management (SCM) | Enhances supplier and distributor coordination, improving inventory and demand forecasting. |
Example
By integrating data warehousing with ERP, a company can analyze historical sales data to forecast future demand, enabling more accurate production planning.
Q5: Briefly describe management information system (MIS) or write a short note on MIS. (Define MIS and ERP.)
Definition of MIS
A Management Information System (MIS) is a structured, computer-based system that collects, processes, and organizes data to provide actionable information for managerial decision-making. MIS supports routine operations by generating reports and summaries tailored to different levels of management.
Key Characteristics of MIS
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Processing | Transforms raw data into information by applying analytical techniques. |
| Structured Reporting | Provides regular reports on operational performance (e.g., sales, inventory, expenses). |
| Exception Reporting | Identifies and highlights deviations from expected performance for management attention. |
| Operational Focus | Designed to support day-to-day management activities and improve organizational control. |
MIS vs ERP
| Feature | MIS | ERP |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Departmental or functional focus | Enterprise-wide integration |
| Data Access | Limited to specific reports | Real-time access across all business units |
| Functionality | Structured, predefined reporting | Automated workflows, analytics, and insights |
Example:
An MIS might generate a monthly payroll report summarizing employee attendance and salaries. An ERP system would automate the entire payroll process, ensuring that changes in attendance records instantly reflect in salary calculations and reporting.
Q6: Which type of information is provided by MIS? How does it differ from DSS? How does MIS differ from DSS? Explain with help of an example. (Why is ERP better than MIS?)
Types of Information Provided by MIS
MIS delivers structured operational data to support routine management activities. It typically includes:
- Financial Reports: Income statements, expense summaries.
- Inventory Reports: Stock levels, replenishment needs.
- Sales Data: Revenue trends, customer orders.
- Employee Information: Attendance, payroll, performance metrics.
Difference between MIS and DSS
A Decision Support System (DSS) is designed to assist in complex decision-making by providing analytical tools, simulations, and “what-if” scenarios. DSS systems can work with semi-structured or unstructured data, offering insights for strategic planning.
| Feature | MIS | DSS |
|---|---|---|
| Data Type | Structured, predefined reports | Semi-structured or unstructured data |
| Purpose | Supports routine operations | Aids in strategic and tactical decisions |
| Tools | Basic reporting | Analytical models, simulations, scenario analysis |
| Example | Monthly sales report | Forecasting future sales based on different scenarios |
Example Comparison:
- An MIS system generates a report showing the company’s monthly revenue.
- A DSS analyzes the impact of price changes on future sales, helping managers plan pricing strategies.
Why ERP is Better than MIS
ERP systems integrate both MIS and DSS functionalities, providing real-time data access and advanced analytics across the organization. This enables both routine and strategic decisions to be made more efficiently.
Example of ERP’s Superiority:
While an MIS might produce a static inventory report, an ERP system would automatically update stock levels as new sales and purchases occur, providing real-time inventory insights.
ERP Introduction – Conclusion
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) represents a comprehensive solution that combines the benefits of both MIS and DSS. While MIS focuses on structured data reporting and operational control, ERP expands this by offering cross-functional data integration and decision support, enabling businesses to thrive in a competitive environment.
By incorporating supporting technologies like business process reengineering, data warehousing, and data mining, ERP ensures that enterprises can harness real-time insights to drive growth and efficiency.
Internal and External References
Links:
- CSVTU Free Resources: CSVTU Official Website
- CSVTU ERP YouTube Playlist: ERP Video Resources
references:
Gatziu, S., & Vavouras, A. (1999). Data Warehousing: Concepts and Mechanisms.
Monk, E., & Wagner, B. (2012). Concepts in Enterprise Resource Planning.
Leon, A. (2014). ERP Demystified. McGraw Hill Education.


