Contents
- Instruction for Students
- 1. What is Innovation, and Why is it Considered an Abstract Concept?
- 2. How Does Innovation Contribute to Economic and Technological Progress?
- 3. What Are the Key Characteristics of an Innovative Idea?
- 4. How Can Innovation Be Measured or Evaluated?
- 5. What Are Some Real-World Examples of Innovative Ideas That Have Shaped Industries?
- Author
Instruction for Students
In this chapter, you will learn:
- The definition of innovation and why it is considered an abstract concept
- The role of innovation in economic and technological progress
- Key characteristics that define an innovative idea
- Methods to measure and evaluate innovation
- Real-world examples of innovation that have transformed industries
This chapter introduces the fundamental nature of innovation, its impact on business and society, and the importance of fostering an innovative mindset.
1. What is Innovation, and Why is it Considered an Abstract Concept?
Definition of Innovation
Innovation refers to the process of generating new ideas, improving existing solutions, and applying novel approaches to solve real-world problems. It can occur in different forms, including technological advancements, business model transformations, or improved processes and services. Unlike simple invention, which focuses on creating something new, innovation emphasizes practical application, adoption, and continuous improvement.
Innovation is essential in economic growth, business development, and technological evolution. It enables industries to adapt to changing consumer demands, enhance efficiency, and foster competitiveness in a dynamic global market. Companies, governments, and organizations continuously invest in innovation to stay ahead of the curve and drive progress.
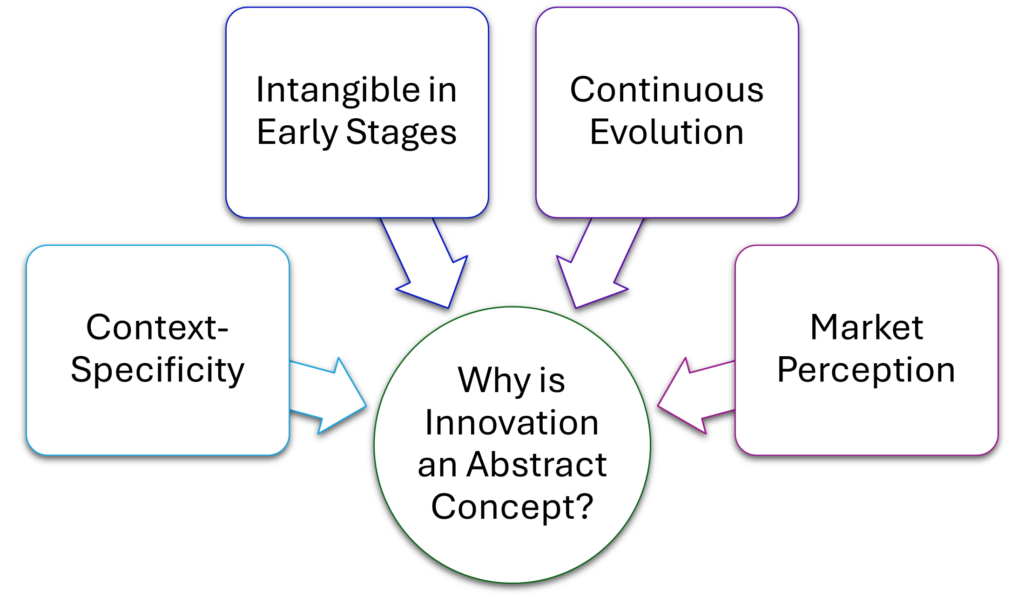
Why is Innovation an Abstract Concept?
Innovation is considered abstract because it is idea-driven and highly dependent on interpretation, context, and execution. It is not a fixed entity or a tangible product but a conceptual process that evolves over time. Several factors contribute to its abstract nature:
- Context-Specificity – What is innovative in one industry may not be in another. For example, automation in manufacturing is groundbreaking, whereas in software, it is a necessity.
- Intangible in Early Stages – Many innovations begin as conceptual ideas or theoretical improvements before materializing into practical solutions.
- Continuous Evolution – Innovation is not a one-time event but an ongoing process of trial, improvement, and refinement.
- Market Perception – What one person sees as innovative, another may view as unnecessary or redundant.
For instance, the development of the internet was once a niche innovation, but today, innovations occur within the internet—such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and blockchain technologies.
Key Takeaway
Innovation is an abstract yet transformative force that drives technological advancement, economic growth, and societal progress. By understanding its fluid nature, businesses and individuals can harness innovation to solve problems, create value, and lead industries into the future.
2. How Does Innovation Contribute to Economic and Technological Progress?
Innovation as a Driver of Economic Growth
Innovation plays a vital role in economic expansion by fostering new industries, increasing productivity, and generating employment opportunities. By introducing better products, services, and business models, innovation drives competition and economic resilience.
Key ways innovation fuels economic progress:
- Job Creation – New industries such as renewable energy, artificial intelligence, and fintech have created millions of new employment opportunities worldwide.
- Increased Productivity – Automation, robotics, and AI-powered tools enhance efficiency, enabling businesses to produce more output with fewer resources.
- Market Competitiveness – Companies that innovate remain market leaders, ensuring they stay relevant and attract new customers.
- Encouraging Entrepreneurship – A thriving innovation ecosystem leads to the emergence of startups and disruptive businesses, fostering economic dynamism.
Example: The Rise of the E-Commerce Industry
The introduction of e-commerce platforms like Amazon and Flipkart revolutionized the retail sector by enabling global reach, lower operational costs, and customer convenience. This innovation reshaped how businesses sell products, eliminating geographical barriers and boosting economic activity.
Innovation as a Catalyst for Technological Advancement
Innovation is also responsible for rapid technological progress across industries. By integrating emerging technologies, businesses can improve products, optimize operations, and address pressing challenges.
Key ways innovation drives technological growth:
- Development of Disruptive Technologies – Breakthroughs such as blockchain, 5G, and quantum computing open new avenues for industries to evolve.
- Medical Advancements – Innovative medical technologies, such as gene editing, AI-based diagnostics, and telemedicine, improve healthcare accessibility and outcomes.
- Sustainability and Green Technologies – The development of solar panels, electric vehicles, and biodegradable materials showcases how innovation supports environmental sustainability.
- Smart Infrastructure – The rise of IoT-powered smart cities and automation has improved efficiency in transportation, energy management, and urban planning.
Example: The Evolution of Smartphones
The smartphone industry has seen continuous innovation, from basic keypad mobile phones to AI-powered, foldable smartphones with 5G connectivity. Companies like Apple, Samsung, and Google have pushed technological boundaries, making smartphones indispensable in modern life.
Key Takeaway
Innovation is a key driver of both economic and technological progress, leading to job creation, industry growth, improved efficiencies, and better solutions for global challenges. Businesses, governments, and individuals must embrace innovation to remain competitive and future-ready.
3. What Are the Key Characteristics of an Innovative Idea?
Understanding Innovative Ideas
An idea is considered innovative when it introduces something new or significantly improves an existing concept, process, or product in a way that provides value. Innovation is not just about originality; it must also be practical, scalable, and beneficial to a target audience.
For an idea to be recognized as innovative, it should possess the following characteristics:
1. Originality and Uniqueness
An innovative idea should offer a fresh perspective or an entirely new approach to solving a problem. Simply replicating existing solutions does not constitute innovation.
Example:
The development of ride-sharing apps like Uber and Lyft transformed urban transportation by offering an on-demand, digital solution to taxi services.
2. Practical Feasibility
A truly innovative idea must be realistically implementable with available resources, technology, or market conditions.
Example:
Self-driving cars are an innovative idea, but without advanced AI, sensors, and regulatory approvals, their full potential remains limited.
3. Scalability and Market Potential
An innovation should have the ability to scale—meaning it can grow beyond small markets and cater to larger audiences or industries.
Example:
E-commerce platforms like Amazon and Alibaba started as niche marketplaces but scaled into global commerce giants.
4. Problem-Solving Capability
Innovative ideas address specific pain points or inefficiencies in existing products, services, or processes.
Example:
Electric vehicles (EVs) like Tesla’s cars solve the problem of fossil fuel dependency and environmental pollution.
5. Sustainability and Longevity
The best innovations are not just trends but offer long-term value and can adapt to changing times.
Example:
The transition from physical music formats (CDs, cassettes) to streaming services like Spotify represents a sustainable innovation that continues to evolve.
Key Takeaway
An innovative idea must be unique, practical, scalable, problem-solving, and sustainable. These characteristics help businesses and entrepreneurs identify which ideas have true disruptive potential.
4. How Can Innovation Be Measured or Evaluated?
Why Measuring Innovation is Important
Since innovation is an abstract concept, businesses and organizations need specific metrics to evaluate its success and impact. Measuring innovation helps companies:
✔️ Identify which innovations bring real economic value.
✔️ Improve decision-making and investment strategies.
✔️ Enhance competitive advantage by focusing on what works.
Key Metrics for Measuring Innovation
1. Market Adoption Rate
Innovation is only successful if people adopt and use the new product or service.
Example:
The adoption of smartphones and mobile internet skyrocketed in the last two decades, proving their innovation value.
2. Return on Investment (ROI)
A business must assess whether its innovative idea generates revenue that exceeds its development and operational costs.
Example:
Companies investing in AI-driven chatbots measure success by analyzing reduced customer service costs and increased efficiency.
3. Competitive Differentiation
Innovation can be measured by how well it differentiates a company from competitors and whether it leads an industry trend.
Example:
Netflix’s shift to subscription-based streaming differentiated it from traditional cable TV and video rentals.
4. Customer Satisfaction and Experience
Successful innovations enhance user experiences and provide higher satisfaction levels.
Example:
Apple’s focus on intuitive design and seamless user experience is a key factor in its global brand loyalty.
5. Industry and Societal Impact
Some innovations extend beyond business success and impact entire industries or societies.
Example:
The invention of renewable energy sources like solar power has long-term environmental benefits and reshapes global energy policies.
Key Takeaway
Innovation must be measured through adoption, financial returns, competitive advantage, customer experience, and industry impact. Businesses that track these metrics can refine their strategies and maximize innovation success.
5. What Are Some Real-World Examples of Innovative Ideas That Have Shaped Industries?
1. E-Commerce: Amazon and Flipkart
Traditional retail transformed with online shopping, allowing global access to goods and revolutionizing supply chains.
Innovation Impact:
- Faster product access.
- Reduction in brick-and-mortar retail dominance.
- AI-powered recommendations personalize shopping.
2. Cloud Computing: AWS and Google Cloud
Instead of using physical servers, businesses now use cloud-based storage for data processing and management.
Innovation Impact:
- Reduces IT infrastructure costs.
- Enables remote work and collaboration.
- Improves data security and scalability.
3. Renewable Energy: Solar and Wind Power
The innovation in clean energy reduces dependence on fossil fuels and combats climate change.
Innovation Impact:
- Reduces carbon footprint.
- Lowers long-term energy costs.
- Creates sustainable employment opportunities.
4. Fintech Revolution: UPI and Blockchain
The rise of digital payments, cryptocurrencies, and decentralized finance (DeFi) has changed the way people handle money.
Innovation Impact:
- Faster, cashless transactions.
- Financial inclusion for underserved regions.
- Blockchain security reduces fraud.
5. Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
AI is being used for diagnosing diseases, automating hospital management, and personalizing medicine.
Innovation Impact:
- Faster and more accurate disease detection.
- Enhances telemedicine and remote patient monitoring.
- Reduces healthcare operational costs.
Key Takeaway
Real-world innovation reshapes industries, creates efficiency, and enhances user experiences. Businesses and individuals that embrace innovation stay ahead in competitive markets.
For more content visit us at our Youtube channel.
